Design in Less Time – A 4-step Kick Start to Designing Learning
By Tara Holwegner, Life Cycle Institute
As appeared in the Learning to Change e-Newsletter
Business changes require that we effectively learn new processes and skills in less time. With the influx of a new workforce and the imminent exit of our most experienced workers, we need to document expertise so that it can become institutional knowledge. In this article, we explore a four-step kick start that can help you capture the critical elements needed for a course in minimal time. After completing the four steps, a learning organization can prioritize development without losing vital intellectual capital.
The Life Cycle Institute believes that learning is a process of alignment, assimilation and application: alignment on learning goals and documenting expectations, participation in a learning event designed and delivered for how adults learn, and application of learning on the job. The four-step kick start described in this article is used to help ensure that the assimilate phase results in learning transfer and leads the learner to apply new understanding and to produce desired outcomes.
Designing and developing a course normally follows a process called ADDIE, which stands for analyze, design, develop, implement and evaluate. Inside the ADDIE process, different methods are used to complete one phase and move on to the next. The four steps in this article come after the “analysis” phase and help move the project from the “design” phase to the “develop” phase.
The four steps to kick-start a learning design are:
- Learning objectives
- Content chunking
- Activity selection
- Sequence course
Let’s take a closer look at each of these elements:
Define learning objectives: what do you want the learners to be able to do after the class? Objectives normally complete the phrase: “after the class, the learner will be able to....” For example, “after the class, the learner will be able to create a new material master form in SAP.” Learning objectives are the foundational element of the course design. You may find that much time is spent trying to reach consensus on what the learning objectives should be. That is appropriate, because every decision made about the course will be based on the learning objectives. If proposed content or activities do not contribute to achieving the learning objective, it does not need to be included in the learning design.
There are several approaches available to help write objectives, including SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, timely) and ABCD (audience, behavior, condition, degree). We consult these approaches, and also use Bloom’s revised taxonomy to help us make a decision about learning objectives. Bloom’s taxonomy is based on verbs that clearly describe the type of behavior we would like to see after the training. For example, if we want someone to be able to communicate the benefits of a new program, a learning objective might be, “Discuss the value that Reliability Excellence can bring to an organization.” Try to keep the learning objectives specific so that it is easy to determine what type of content and activities we will need to reach them.
Chunk the content: Determine the main subjects or topics that are “need to know” to achieve the learning objectives. These main subjects should be high-level words or short phrases that describe the main points of the major modules in the course. We normally take each learning objective and quickly jot down the core content components essential to being able to perform at the level of the learning objective. Normally these first impressions of subjects are the most “pure,” meaning they don’t include excessive amounts of “nice to know” information.
Activities: How will we get learners to work with the content? Each topic should have some sort of interaction, some way that the participant is working with the information. If you’re using Bloom’s to help define your objectives, the activity should match the Bloom’s level of the learning objective.
Sequence: After we’ve defined content and activity ideas, we typically sequence content and activities to get an idea of flow.
To ensure that all four elements are defined in a cohesive, efficient manner, we schedule a meeting with the design partner and interested stakeholders to define the four elements. Depending on the scope of the training, these meetings can last from two hours to an entire day. The deliverable from this meeting is a document that comprises the critical elements needed to develop a course.
There are five primary benefits to this approach:
- The essential elements of the course are defined in one meeting, speeding time to development
- Portions of the course can be divided and prioritized between team members to capitalize on available resources
- Design team members agree on the content and activities expected, so a level of effort can be anticipated and limits the “it’s not my action item” mindset
- Design team members can more easily schedule time to develop when working on multiple projects
- Communication and internal/external marketing for the course can start immediately, jump-starting any change management efforts for mandatory or new initiative-based training
To organize and document the four-step design kick start, we typically use a grid-like template that helps us sequence content and activities and gives us a picture of the day. This could be captured in many different ways, including using smartboard, tablet, or marker boards and flip charts.
Below is one example of how you can organize your content and activities in one place:
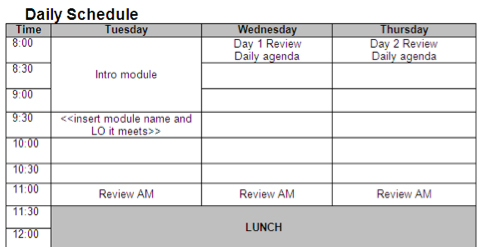
Once the four steps -- learning objectives, content, activities and sequence -- are documented, they make a course map that guides the rest of the project. This is an early design document, so elements of this “Course Summary” may change; however, as long as the learning objectives do not change drastically, neither does your summary.
Defining up front the four steps critical to course design provides benefits early in the course development process for team members and potential learners alike. Among the benefits are:
- Early buy-in from team members and stakeholders
- More efficient resource scheduling
- Clearer expectations and level of effort for team members
- Early awareness for potential learners
For more information about how the Life Cycle Institute can help your learning programs yield more effective results, please contact us at: education@LCE.com.
Tara Holwegner is a Learning Consultant with the Life Cycle Institute. Tara has designed and delivered formal and informal learning events and training material since 2001. Her passion for adult learning principles leads her to build learning products that meet business objectives and practice facilitation techniques that ensure knowledge transfer. Tara’s learning products have been named a finalist in training product competitions; her flexibility allows her to work on a range of projects, from advising a Fortune 500 company on an internal certification program to delivering Web training seminars. You can reach Tara at tholwegner@LCE.com.
© Life Cycle Engineering, Inc.

For More Information
843.744.7110 | info@LCE.com
